| دانلود رایگان مقاله انگلیسی + خرید ترجمه فارسی | |
| عنوان فارسی مقاله: |
سنجش خصوصیات مکانی و زمانی نشست زمین، تخلیه آب زیرزمینی و ضخامت لایه تراکم پذیر در دشت پکن، چین |
| عنوان انگلیسی مقاله: |
Measuring Spatiotemporal Features of Land Subsidence, Groundwater Drawdown, and Compressible Layer Thickness in Beijing Plain, China |
|
|
|
| مشخصات مقاله انگلیسی (PDF) | |
| سال انتشار | 2017 |
| تعداد صفحات مقاله انگلیسی | 17 صفحه با فرمت pdf |
| رشته های مرتبط با این مقاله | زمین شناسی |
| گرایش های مرتبط با این مقاله | زمین شناسی مهندسی و زمین شناسی زیست محیطی |
| چاپ شده در مجله (ژورنال) | آب – Water |
| کلمات کلیدی | فرونشست زمین، افت آب زیر زمینی، لایه تراکم پذیر، مرکز ثقل، بیضی انحرافی استاندارد |
| ارائه شده از دانشگاه | دانشکده منابع محیطی و گردشگری، چین |
| نویسندگان | Yongyong Li, Huili Gong, Lin Zhu and Xiaojuan Li |
| شناسه شاپا یا ISSN | ISSN 2073-4441 |
| شناسه دیجیتال – doi | https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010064 |
| رفرنس | دارد ✓ |
| کد محصول | 9501 |
| لینک مقاله در سایت مرجع | لینک این مقاله در نشریه MDPI |
| نشریه MDPI |  |
| مشخصات و وضعیت ترجمه فارسی این مقاله (Word) | |
| وضعیت ترجمه | انجام شده و آماده دانلود |
| کیفیت ترجمه | طلایی⭐️ |
| تعداد صفحات ترجمه تایپ شده با فرمت ورد با قابلیت ویرایش | 22 صفحه با فونت 14 B Nazanin |
| ترجمه عناوین تصاویر و جداول | ترجمه شده است ✓ |
| ترجمه متون داخل تصاویر | ترجمه نشده است ☓ |
| ترجمه متون داخل جداول | ترجمه شده است ✓ |
| درج تصاویر در فایل ترجمه | درج شده است ✓ |
| درج جداول در فایل ترجمه | درج شده است ✓ |
| درج فرمولها و محاسبات در فایل ترجمه | به صورت عکس درج شده است ✓ |
| منابع داخل متن | به صورت عدد درج شده است ✓ |
| فهرست مطالب |
|
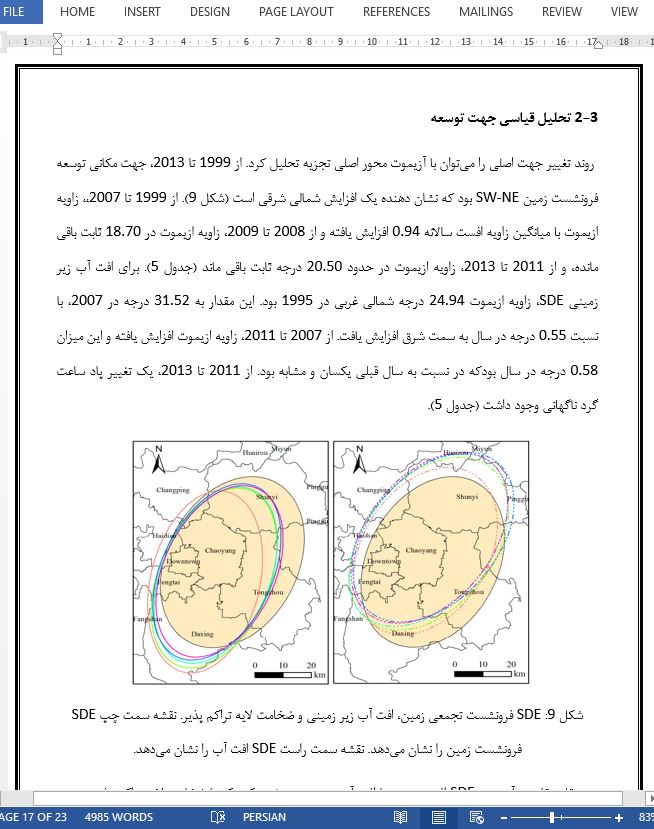
چکیده 1- مقدمه 2- مواد و روشها 2-1 مطالعه موردی 2-2 مجموعه دادههای موجود 2-3 تحلیل مرکز ثقل 2-4 تحلیل بیضی انحرافی استاندارد 3- نتایج 3-1 تحلیل تغییرات مرکز ثقل 3-1-1 مرکز ثقل فرونشست زمین 3-1-2 مرکز ثقل افت آب زیر زمینی و ضخامت لایه تراکم پذیر 3-1-1 تحلیل مزدوج مرکز ثقل 3-2 تحلیل قیاسی جهت توسعه 3-2 تحلیل قیاسی روند توزیع و پراکنش 4-3 تحلیل قیاسی ضریب تمایز مکانی 4- بحث 5- نتیجه گیری |
| بخشی از ترجمه |
|
چکیده پکن بر روی چندین مخروط افکنه آبرفتی و کوهرفتی با رسوبات تحکیم نیافته کواترنری ضخیم واقع شده است. این شهر به دلیل بهره برداری از آب زیر زمینی به شدت در معرض فرونشست زمین و افت جدی آب زیر زمینی میباشد. هدف این مطالعه معرفی روشهای اندازه گیری توزیع جغرافیایی در تحقیقات فرونشست زمین برای سنجش ویژگیهای جغرافیایی، فرونشست زمین، افت زیرزمینی و ضخامت لایه تراکم پذیر است. بنابراین، ما از تحلیل مرکز ثقل و روشهای بیضی استاندارد (SDE) در GIS به منظور تحلیل آماری تمایل غلظت، جهت اصلی، روند پراکنش و تفاوتهای توزیعی در 1995(1999)،2007، 2009، 2011 و 2013 استفاده کردیم. نتایج نشان میدهد که آنها همگی در منطقه چائویانگ پکن متمرکز هستند. روند تمرکز فرونشست زمین با روند افت آب زیر زمینی متمرکز بود. جهت اصلی فرونشست زمین جنوب غربی- شمال شرقی بود که بیشتر مشابه با توزیع مکانی استاتیک لایه تراکم پذیر بود. روند انتشار و پراکنش فرونشست زمین نزدیک به لایه تراکم پذیر با افزایش شدت آن بود. اختلاف توزیع مکانی بین فرونشست زمین و افت آب زیر زمینی حدود 0.2 بود و اختلاف بین فرونشست زمین و ضخامت لایه تراکم پذیر از 0.22 تا 0.07 کاهش یافت و این نشان میدهد که الگوی توزیع مکانی فرونشست زمین به شدت نزدیک به الگوی لایه تراکم پذیر بود. نتایج این مطالعه برای ارزیابی توزیع توسعه فرونشست زمین و مدیریت منابع آب زیر زمینی مفید است.
5- نتیجه گیری |
| بخشی از مقاله انگلیسی |
|
Abstract Beijing is located on multiple alluvial-pluvial fans with thick Quaternary unconsolidated sediments. It has suffered serious groundwater drawdown and land subsidence due to groundwater exploitation. This study aimed to introduce geographical distribution measure methods into land subsidence research characterizing, geographically, land subsidence, groundwater drawdown, and compressible layer thickness. Therefore, we used gravity center analysis and standard deviational ellipse (SDE) methods in GIS to statistically analyze their concentration tendency, principle orientation, dispersion trend, and distribution differences in 1995 (1999), 2007, 2009, 2011, and 2013. Results show that they were all concentrated in Chaoyang District of Urban Beijing. The concentration trend of land subsidence was consistent with that of groundwater drawdown. The principle orientation of land subsidence was SW–NE, which was more similar with that of the static spatial distribution of the compressible layer. The dispersion tendency of land subsidence got closer to that of the compressible layer with its increasing intensity. The spatial distribution difference between land subsidence and groundwater drawdown was about 0.2, and that between land subsidence and compressible layer thickness it decreased from 0.22 to 0.07, reflecting that the spatial distribution pattern of land subsidence was increasingly close to that of the compressible layer. Results of this study are useful for assessing the distribution of land subsidence development and managing groundwater resources.
5- Conclusions This paper proposed a comprehensive geographic measurement to improve the understanding of spatiotemporal distribution features of land subsidence, groundwater drawdown, and compressible layer thickness in Beijing Plain. Land subsidence, groundwater drawdown, and compressible layer thickness were all concentrated in Chaoyang District. The concentration of land subsidence moved from southwest to northeast, which was basically consistent with groundwater drawdown. The compressible layer thickness was concentrated in the east-central Chaoyang District on, or close to, the alluvial-pluvial fan-fringe areas with mass compressible deposits. The principle direction of land subsidence was SE–NE. It changed with that of the groundwater drawdown, but was getting closer to that of the compressible layer. The length ratio between the major and minor axes suggested that the dispersion tendency of the land subsidence became closer to that of the compressible layer with its increasing development intensity. The spatial contraction of the ellipse suggested the Chaoyang District, in the central region of the study area, experienced more serious subsidence than that in the surrounding areas most of the time.
|
|
تصویری از مقاله ترجمه و تایپ شده در نرم افزار ورد |
|
|
| دانلود رایگان مقاله انگلیسی + خرید ترجمه فارسی | |
| عنوان فارسی مقاله: |
سنجش خصوصیات مکانی و زمانی نشست زمین، تخلیه آب زیرزمینی و ضخامت لایه تراکم پذیر در دشت پکن، چین |
| عنوان انگلیسی مقاله: |
Measuring Spatiotemporal Features of Land Subsidence, Groundwater Drawdown, and Compressible Layer Thickness in Beijing Plain, China |
|
|
|