این مقاله انگلیسی ISI در نشریه الزویر در 8 صفحه در سال 2022 منتشر شده و ترجمه آن 21 صفحه میباشد. کیفیت ترجمه این مقاله ویژه – طلایی ⭐️⭐️⭐️ بوده و به صورت کامل ترجمه شده است.
| دانلود رایگان مقاله انگلیسی + خرید ترجمه فارسی | |
| عنوان فارسی مقاله: |
مدل مراقبت های اولیه برای غربالگری و درمان افسردگی: گزارش وایتل ساین6 از یک همگروه دوم با 32106 بیمار |
| عنوان انگلیسی مقاله: |
A primary care first (PCP-first) model to screen and treat depression: A VitalSign6 report from a second cohort of 32,106 patients |
|
|
|
| مشخصات مقاله انگلیسی | |
| فرمت مقاله انگلیسی | pdf و ورد تایپ شده با قابلیت ویرایش |
| سال انتشار | 2022 |
| تعداد صفحات مقاله انگلیسی | 8 صفحه با فرمت pdf |
| نوع مقاله | ISI |
| نوع نگارش | مقاله پژوهشی (Research article) |
| نوع ارائه مقاله | ژورنال |
| رشته های مرتبط با این مقاله | روانشناسی |
| گرایش های مرتبط با این مقاله | روانشناسی بالینی |
| چاپ شده در مجله (ژورنال) | روانپزشکی بیمارستان عمومی – General Hospital Psychiatry |
| کلمات کلیدی | وایتال ساین 6 (Vitalsign6)، غربالگری افسردگی، پایش افسردگی با استفاده از مراقبت های مبتنی بر سنجش، مراقبت اولیه |
| کلمات کلیدی انگلیسی | VitalSign6 – Depression screening – Depression monitoring |
| ارائه شده از دانشگاه | مرکز تحقیقات افسردگی و مراقبت های بالینی، گروه روانپزشکی، ایالات متحده |
| نمایه (index) | scopus – master journals – JCR – MedLine |
| نویسندگان | Margaret Z. Wang – Manish K. Jha – Abu Minhajuddin – Ronny Pipes – Sara Levinson -Taryn L. Mayes – Tracy L. Greer – Madhukar H. Trivedi |
| شناسه شاپا یا ISSN | 0163-8343 |
| شناسه دیجیتال – doi | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2021.11.001 |
| ایمپکت فاکتور(IF) مجله | 2.431 در سال 2020 |
| شاخص H_index مجله | 103 در سال 2021 |
| شاخص SJR مجله | 1.211 در سال 2020 |
| شاخص Q یا Quartile (چارک) | Q1 در سال 2020 |
| بیس | نیست ☓ |
| مدل مفهومی | ندارد ☓ |
| پرسشنامه | ندارد ☓ |
| متغیر | ندارد ☓ |
| فرضیه | ندارد ☓ |
| رفرنس | دارای رفرنس در داخل متن و انتهای مقاله ✓ |
| کد محصول | 12237 |
| لینک مقاله در سایت مرجع | لینک این مقاله در سایت Elsevier |
| نشریه | الزویر – Elsevier |
| مشخصات و وضعیت ترجمه فارسی این مقاله | |
| فرمت ترجمه مقاله | pdf و ورد تایپ شده با قابلیت ویرایش |
| وضعیت ترجمه | انجام شده و آماده دانلود |
| کیفیت ترجمه | ویژه – طلایی ⭐️⭐️⭐️ |
| تعداد صفحات ترجمه تایپ شده با فرمت ورد با قابلیت ویرایش | 21 (2 صفحه رفرنس انگلیسی) صفحه با فونت 14 B Nazanin |
| ترجمه عناوین تصاویر و جداول | ترجمه شده است ✓ |
| ترجمه متون داخل تصاویر | ترجمه شده است ✓ |
| ترجمه متون داخل جداول | ترجمه شده است ✓ |
| ترجمه ضمیمه | ندارد ☓ |
| ترجمه پاورقی | ندارد ☓ |
| درج تصاویر در فایل ترجمه | درج شده است ✓ |
| درج جداول در فایل ترجمه | درج شده است ✓ |
| درج فرمولها و محاسبات در فایل ترجمه | ندارد ☓ |
| منابع داخل متن | به صورت عدد درج شده است ✓ |
| منابع انتهای متن | به صورت انگلیسی درج شده است ✓ |
| فهرست مطالب |
| چکیده 1 مقدمه 2 مواد و روش ها 2-1 مکان های درمانگاهی 2-2 غربالگری افسردگی همگانی 2-3 خودگزارشی های VS6 بیش تر برای بیمارانی با نتیجه ی غربالگری مثبت به ازای PHQ-2 2-4 تشخیص بالینی بیمارانی با غربالگری مثبت 2-5 درمان و پایش بیمارانی دچار افسردگی 2-6 تحلیل های آماری 3 نتایج 3-1 بیمارانی با غربالگری مثبت بر اساس PHQ-2 3-2 بیمارانی با تشخیص افسردگی 3-4 ملاقات های تکمیلی برای بیمارانی دچار افسردگی و دست کم 18 هفته ثبت نام 3-5 بهبودی بیماران افسرده تحت دارودرمانی و مراقبت مبتنی بر سنجش و 1پیگیری یا بیش تر 4 بحث منابع |
| بخشی از ترجمه |
|
چکیده |
| بخشی از مقاله انگلیسی |
|
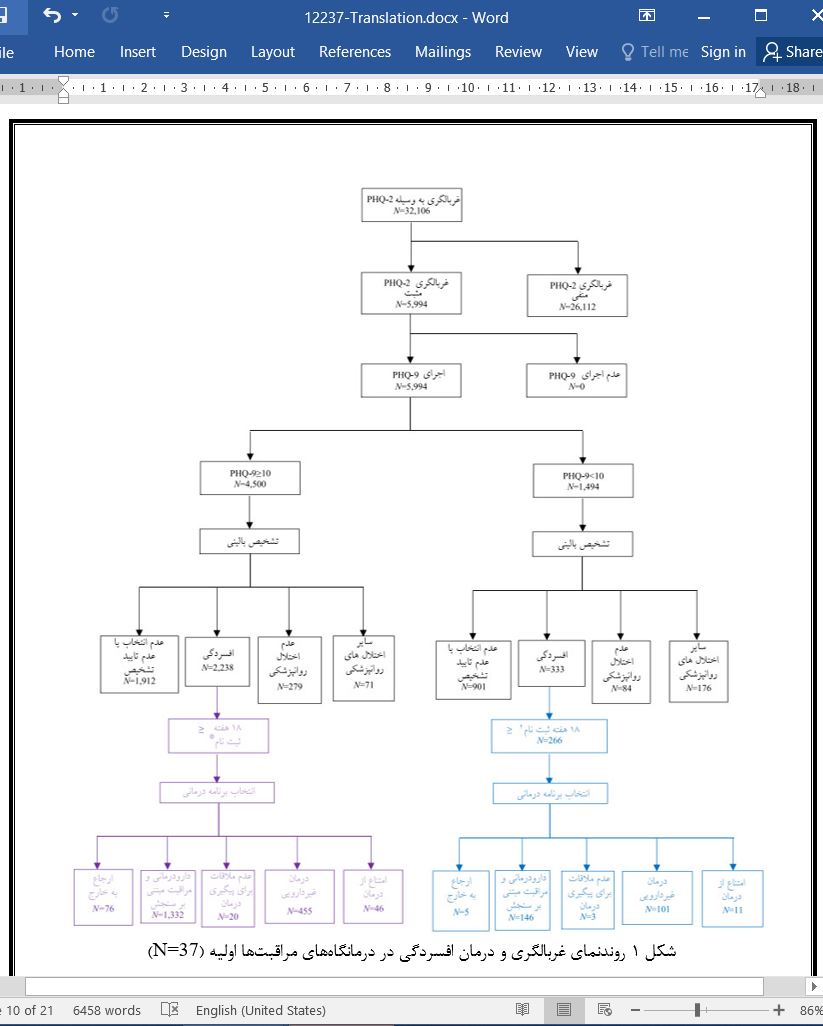
Abstract Purpose This report from VitalSign6 project describes treatment selection, follow-up rates and remission outcomes by initial depression severity using the PCP-FIRST model. Methods This retrospective analysis included 32,106 patients aged ≥12 years screened with the Patient Health Questionnaire 2-item (PHQ-2) from November 2016 to July 2019 across 37 primary care clinics. PHQ-2 positive-screen patients (PHQ-2 ≥ 3) received 9-item PHQ (PHQ-9) and 7-item Generalized Anxiety Disorder scales, clinician assessments, and evaluation for pharmacotherapy management with measurement-based care (MBC). Results Of PHQ-2 screened patients, 18.7% (5994/32,106) were positive and received a PHQ-9. Of 5994 patients with PHQ-9, 2571 received a clinical diagnosis of depression of whom, 333 had none-mild depression (PHQ-9 < 10) and 2238 had moderate-severe depression (PHQ-9 ≥ 10). Of the 333 patients with none-mild depression and 2238 patients with moderate-severe depression, 266 and 1929 had at least 18 weeks of data available. Of these, 54.9% (146/266) with none-mild depression and 69.1% (1332/1929) with moderate-severe depression were started on pharmacotherapy. Of the 1478 patients with clinical diagnosis of depression, initiated on pharmacotherapy, 1046 returned for ≥1 follow-up and 616 returned for ≥3 follow-ups over 18 weeks. Of the 1046 patients with ≥1 follow-up visit within 18 weeks, remission rates for patients with mild depression, moderate-severe depression, and overall were 55.6% (66/99), 30% (282/941), and 32.4% (338/1040) respectively. Conclusions Despite this being a real-world, usual care sample, remission outcomes exceed real world remission rate expectations of 6% in primary care. 1 Introduction Major depressive disorder (MDD) affects up to 10% of adults in the United States annually, but the use of effective treatments is suboptimal with an average of eight years between onset of MDD to treatment initiation [1,2]. The United States Preventative Services Task Force (USPSTF) has recommended universal screening for depression in individuals 12 years or older [3,4]. Depression screening and treatment in outpatient settings, however, remains poor, with over half of MDD cases being undetected [5–7]. In a national cross-sectional study of U.S. outpatient primary care visits, as few as 3% to 4% involved depression screening [8]. 4 Discussion This report evaluated the treatment selection and follow-up rates for patients with none-mild versus moderate-severe depression and the remission outcomes of patients with mild versus moderate-severe depression treated with MBC pharmacotherapy over 18 weeks across 37 under-resourced primary care clinics in this quality improvement program. As expected, more patients with moderate-severe depression than mildly depressed patients were treated with pharmacotherapy. Overall, of patients treated with MBC pharmacotherapy that returned for at least one follow-up visit and were enrolled for 18 weeks, 32.4% (338/1040) of those with PHQ-9 ≥ 5 reached remission. Of patients with mild depression that returned at least once, 55.6% (56/99) were in remission at 18 weeks, while 30% (282/941) of patients with moderatesevere depression reached remission. Importantly, rates of remission improved with number of follow-ups, with those having at least 3 follow-up visits having the greatest remission rate. Our PCP-First approach results are comparable to real-world collaborative care outcomes and also suggest further benefits if the two approaches are combined [21,22]. Three-fourths of patients diagnosed with depression returned at least once, and overall attrition improved compared to the first VitalSign6 cohort, which were 30.2%, 12.6%, and 11.6% for 1, 2, and ≥ 3 follow-up visits, respectively. |
|
تصویری از مقاله ترجمه و تایپ شده در نرم افزار ورد |
|
|
| دانلود رایگان مقاله انگلیسی + خرید ترجمه فارسی | |
| عنوان فارسی مقاله: |
مدل مراقبت های اولیه برای غربالگری و درمان افسردگی: گزارش وایتل ساین6 از یک همگروه دوم با 32106 بیمار |
| عنوان انگلیسی مقاله: |
A primary care first (PCP-first) model to screen and treat depression: A VitalSign6 report from a second cohort of 32,106 patients |
|
|
|