این مقاله انگلیسی ISI در نشریه ساینس دایرکت (الزویر) در 6 صفحه در سال 2018 منتشر شده و ترجمه آن 16 صفحه میباشد. کیفیت ترجمه این مقاله ویژه – طلایی ⭐️⭐️⭐️ بوده و به صورت کامل ترجمه شده است.
| دانلود رایگان مقاله انگلیسی + خرید ترجمه فارسی | |
| عنوان فارسی مقاله: |
برآورد عملکرد تشخيصی چهار رویکرد جهت تشخيص ژيارديا دئوسناليس در نمونه های مدفوع انسان، سگ و گربه ناقل |
| عنوان انگلیسی مقاله: |
Assessment of the diagnostic performance of four methods for the detection of Giardia duodenalis in fecal samples from human, canine and feline carriers |
|
|
|
| مشخصات مقاله انگلیسی (PDF) | |
| سال انتشار | 2018 |
| تعداد صفحات مقاله انگلیسی | 6 صفحه با فرمت pdf |
| نوع مقاله | ISI |
| نوع نگارش | مقاله پژوهشی (Research Article) |
| نوع ارائه مقاله | ژورنال |
| رشته های مرتبط با این مقاله | زیست شناسی و پزشکی |
| گرایش های مرتبط با این مقاله | انگل شناسی پزشکی و میکروبیولوژی |
| چاپ شده در مجله (ژورنال) | مجله روشهای میکروبیولوژی – Journal of Microbiological Methods |
| کلمات کلیدی | ELISA، تکنیک شناورسازی، ژيارديا دئوسناليس، ایمونوكروماتوگرافی، PCR |
| کلمات کلیدی انگلیسی | ELISA, Faust technique, Giardia duodenalis, Immunochromatography, PCR |
| ارائه شده از دانشگاه | گروه میکروبیولوژی و انگل شناسی، مؤسسه پزشکی، دانشگاه فلومانمینس (UFF)، برزیل |
| نویسندگان | Flávia Fernandes de Mendonça Uchôa, Adriana Pittella Sudré, Sabrina Destri Emmerick Campos, Nádia Regina PereiraAlmosny |
| نمایه (index) | Scopus – Master journals – JCR – MedLine |
| شناسه شاپا یا ISSN | ISSN 0167-7012 |
| شناسه دیجیتال – doi | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2018.01.001 |
| ایمپکت فاکتور(IF) مجله | 1.805 در سال 2018 |
| شاخص H_index مجله | 120 در سال 2019 |
| شاخص SJR مجله | 0.699 در سال 2018 |
| شاخص Q یا Quartile (چارک) | Q3 در سال 2018 |
| بیس | نیست ☓ |
| مدل مفهومی | ندارد ☓ |
| پرسشنامه | ندارد ☓ |
| متغیر | ندارد ☓ |
| رفرنس | دارای رفرنس در داخل متن و انتهای مقاله ✓ |
| کد محصول | 9440 |
| لینک مقاله در سایت مرجع | لینک این مقاله در نشریه Elsevier |
| نشریه الزویر |  |
| مشخصات و وضعیت ترجمه فارسی این مقاله (Word) | |
| وضعیت ترجمه | انجام شده و آماده دانلود در فایل ورد و PDF |
| کیفیت ترجمه | ویژه – طلایی ⭐️⭐️⭐️ |
| تعداد صفحات ترجمه تایپ شده با فرمت ورد با قابلیت ویرایش | 16 صفحه با فونت 14 B Nazanin |
| ترجمه عناوین جداول | ترجمه شده است ✓ |
| ترجمه متون داخل جداول | ترجمه شده است ✓ |
| درج جداول در فایل ترجمه | درج شده است ✓ |
| منابع داخل متن | به صورت انگلیسی درج شده است ✓ |
| فهرست مطالب |
|
چکیده |
| بخشی از ترجمه |
|
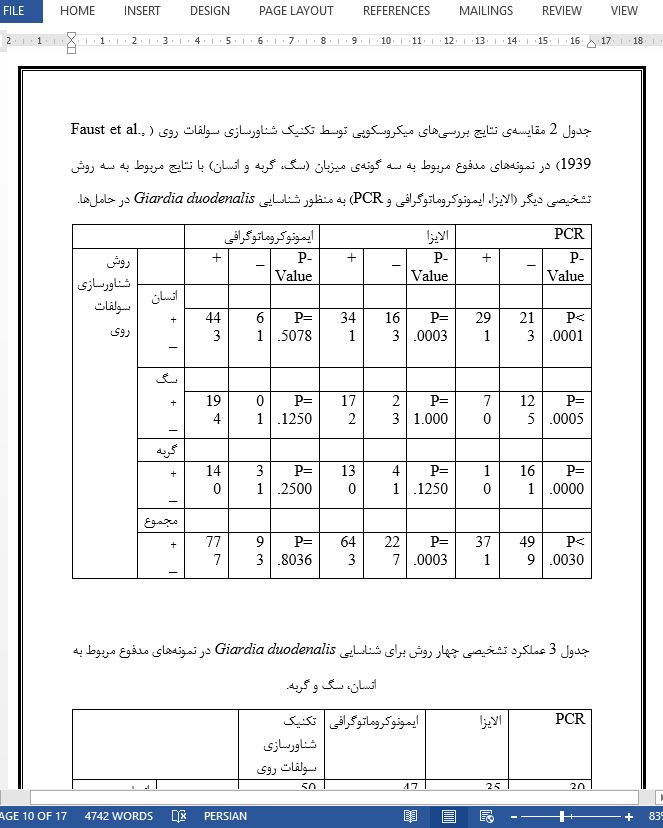
چکیده بیماری های انگلی روده، از جمله ژیاردیا، از نظر سلامت عمومی مورد توجه هستند. روش های مختلفی برای تشخیص این عفونت انگلی در نمونه های مدفوع مانند شناسایی کیست های پروتوزوآ و تروفوزوئیت ها با استفاده از میکروسکوپ نوری، شناسایی آنتی ژن های خاص توسط ELISA و تکثیر قطعات DNA با استفاده از PCR در دسترس هستند. هدف از این مطالعه، بررسی عملکرد چهار تست آزمایشگاهی برای تشخیص Giardia duodenalis در نمونه های مدفوع از سه گونه میزبان متفاوت با تشخیص قبلی ژیاردیا است. سگ، گربه و انسان بیمار نمونه های مدفوع جدیدی را برای آزمایش دوباره ی ژیاردیا قبل از آغاز درمان با داروهای ضد پروتوزا فراهم کردند. برای این منظور، نمونه های مدفوع سه گانه از 54 انسان، 24 سگ و 18 گربه در شهر Niterói، RJ، جنوب شرقی برزیل، با میکروسکوپ نوری، ELISA، ایمونوكروماتوگرافی و PCR آشیانه ای مورد بررسی قرار گرفتند. روش شناورسازی سانتریفیوژی، کیست های ژیاردیا را در 6/89 درصد (96/86) از نمونه های مدفوع تشخیص داد. پروتوزای انگل از طریق ايمونوكروماتوگرافی در 5/87٪ (96/84) از این نمونه ها تشخیص داده شد. ژیاردیا توسط ELISA در 8/69٪ (96/67) از نمونه مدفوع ناقلین با تشخیص قبلی عفونت ژیاردیا تشخیص داده شد. ژیاردیا با استفاده از PCR تنها در 6/39٪ (96/38) از نمونه های مدفوع تشخیص داده شد. براساس این یافته ها، پیشنهاد می کنیم که از میان این چهار آزمایش که در این مطالعه استفاده شده است، تکنیک شناورسازی روی سولفات (Faust et al., 1939) بهترین آزمایش تشخیصی از نظر حساسیت و اختصاصی بودن برای تشخیص G. duodenalis در نمونه های جمع آوری شده از سگ، گربه و انسان است.
4- نتیجه گیری |
| بخشی از مقاله انگلیسی |
|
Abstract Enteric parasitic diseases including giardiasis are of public health concern. Different methods are available for the diagnosis of this parasitic infection in fecal samples such as the identification of protozoan cysts and trophozoites by light microscopy, detection of specific antigens by ELISA, and amplification of DNA fragments by PCR. The present study aimed at assessing the performance of four laboratory tests for the detection of Giardia duodenalis in fecal specimens from three different host species with a previous diagnosis of giardiasis; canine, feline and human patients provided new stool samples to be retested for Giardia before initiating treatment with antiprotozoal drugs. For this purpose, triplicate fecal specimens from 54 humans, 24 dogs and 18 cats living in the city of Niterói, RJ, southeast Brazil, were analysed by light microscopy, ELISA,immunochromatography, and nested PCR. The centrifugal-flotation method detected Giardia cysts in 89.6% (86/96) of the fecal samples. The protozoan parasite was detected via immunochromatography in 87.5% (84/96) of these samples. Giardia was detected by ELISA in 69.8% (67/96) of the stool specimens from carriers with a previous diagnosis of Giardia infection. Giardia was detected by PCR in only 39.6% (38/96) of the fecal specimens. Based on these findings, we suggest that, among the four assays that were used in this study, the zinc sulphate flotation technique (Faust et al., 1939) is the best diagnostic assay in terms of sensitivity and specificity to detect G. duodenalis on serially collected samples from dogs, cats and humans.
4- Conclusion Since a definitive diagnosis of giardiasis can be challenging due to a number of factors including intermittent shedding of cysts in feces and low numbers of cysts in stool specimens, if a test comes back negative, it is recommended that the fecal sample be tested by a different diagnostic test in order to completely rule out Giardia duodenalis infection. In this context, the use of a combination of diagnostic methods seems to be a good strategy in the diagnosis of this protozoan disease. Based on our findings and comparing our results with the results of other studies previously published by other authors, we suggest that the zinc sulphate flotation technique is the best laboratory test for the diagnosis of giardiasis. This method is a low cost diagnostic test that can detect multiple parasitic infections and performs well when serial fecal samples are tested. Immunological techniques, especially immunochromatography, can be used as alternative diagnostic methods but these are expensive, sensitive and specific tests that do not detect enteric parasites other than Giardia. Therefore, immunological assays should be used in those cases in which light microscopy yields negative results. PCR technique allows molecular characterization of Giardia duodenalis isolates which are of paramount importance in epidemiological studies. However, PCR was not able to detect light infections in feces of asymptomatic carriers with low parasitic loads especially animals.
|
|
تصویری از مقاله ترجمه و تایپ شده در نرم افزار ورد |
|
|
| دانلود رایگان مقاله انگلیسی + خرید ترجمه فارسی | |
| عنوان فارسی مقاله: |
برآورد عملکرد تشخيصی چهار رویکرد جهت تشخيص ژيارديا دئوسناليس در نمونه های مدفوع انسان، سگ و گربه ناقل |
| عنوان انگلیسی مقاله: |
Assessment of the diagnostic performance of four methods for the detection of Giardia duodenalis in fecal samples from human, canine and feline carriers |
|
|
|