این مقاله انگلیسی ISI در نشریه ساینس دایرکت (الزویر) در 10 صفحه در سال 2017 منتشر شده و ترجمه آن 24 صفحه میباشد. کیفیت ترجمه این مقاله ویژه – طلایی ⭐️⭐️⭐️ بوده و به صورت کامل ترجمه شده است.
| دانلود رایگان مقاله انگلیسی + خرید ترجمه فارسی | |
| عنوان فارسی مقاله: |
تحقیقات تجربی در رابطه با رفتار سطوح مشترک بین بتن – بتن تحت ترکیبی از تکانه های برشی و خمشی |
| عنوان انگلیسی مقاله: |
Experimental research on the behaviour of concrete-to-concrete interfaces subjected to a combination of shear and bending moment |
|
|
|
| مشخصات مقاله انگلیسی (PDF) | |
| سال انتشار | 2017 |
| تعداد صفحات مقاله انگلیسی | 10 صفحه با فرمت pdf |
| رشته های مرتبط با این مقاله | مهندسی عمران |
| گرایش های مرتبط با این مقاله | سازه، مدیریت ساخت و زلزله |
| چاپ شده در مجله (ژورنال) | سازه های مهندسی – Engineering Structures |
| کلمات کلیدی | بتن- بتن، نیروی برشی، اصطکاک برشی، ساخت توسعه یافته |
| ارائه شده از دانشگاه | دانشگاه لیسبون، پرتغال |
| نویسندگان | Eduardo Cavaco , José Camara |
| شناسه شاپا یا ISSN | ISSN 0141-0296 |
| شناسه دیجیتال – doi | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2016.11.041 |
| رفرنس | دارد ✓ |
| کد محصول | 9452 |
| لینک مقاله در سایت مرجع | لینک این مقاله در نشریه Elsevier |
| نشریه الزویر |  |
| مشخصات و وضعیت ترجمه فارسی این مقاله (Word) | |
| وضعیت ترجمه | انجام شده و آماده دانلود |
| کیفیت ترجمه | ویژه – طلایی ⭐️⭐️⭐️ |
| تعداد صفحات ترجمه تایپ شده با فرمت ورد با قابلیت ویرایش | 24 صفحه با فونت 14 B Nazanin |
| ترجمه عناوین تصاویر و جداول | ترجمه شده است ✓ |
| ترجمه متون داخل تصاویر | ترجمه نشده است ☓ |
| ترجمه متون داخل جداول | ترجمه شده است ✓ |
| درج تصاویر در فایل ترجمه | درج شده است ✓ |
| درج جداول در فایل ترجمه | درج شده است ✓ |
| درج فرمولها و محاسبات در فایل ترجمه | به صورت عکس درج شده است ✓ |
| منابع داخل متن | درج نشده است ✓ |
| فهرست مطالب |
|
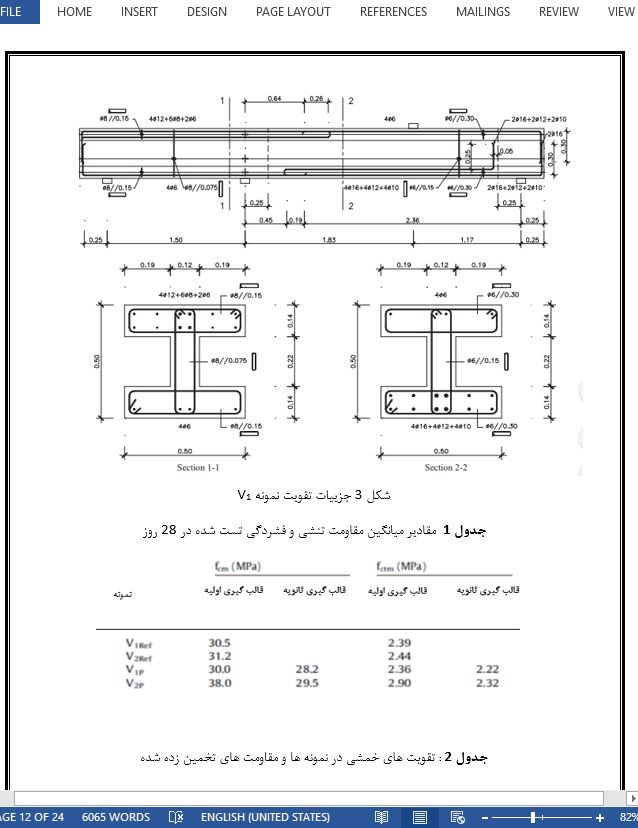
چکیده 1- مقدمه نشانه ها 2- مروری بر مقالات 2-1 نظریه اصطکاک برشی 2-2 عبارات طراحی 2-3 تاثیر بی قاعدگی 3- تحقیقات آزمایشی 4- نتایج 5- مباحث 6- جمع بندی |
| بخشی از ترجمه |
|
چکیده مقاومت برشی سطوح مشترک بتن – بتن تحت تاثیر نیرو های برشی یا نیرو های نرمال عمود نسبت به سطح، یا ترکیبی از این دو با استفاده از نظریه اصطکاک برشی مورد بررسی قرار گرفته است که این نظریه در دهه 60 برای اتصالات ساختار های پیش ساخت توسعه یافته است. نظریه اصطکاک برشی با در نظر داشتن شکست برشی به صورت لغزش خالص توسعه یافته است و در ترکیب با ترک های تنشی نبوده است و این روش در بیشتر قوانین طراحی در سراسر جهان مورد استفاده قرار میگیرد. با وجود این که بهبود های مختلفی در نظریه اصلی در 50 سال اخیر ایجاد شده است، مطالعه های محدودی به بررسی و رفع مشکلات رفتار سطوح تحت تاثیر ترکیب تکانه های برشی و خمشی پرداخته اند، که در این شریط یک لغزش برشی ممکن است در راستای یک ترک تنشی ایجاد شود و یک منطقه فشردگی ایجاد کند. این شرایط یکی از مشکلات مرتبط برای طراحی ساختار های بتنری تقویت شده پیش ساخت یا بتن های قالب گیری شده در محل، میباشد. این مقاله یک کار آزمایشی را ارائه میدهد که به بررسی رفتار سطوح مشترک بتن به بتن تحت تاثیر ترکیبی از تکانه های برشی و خمشی پرداخته است. تاثیر سطح مشترک بر روی رفتار کلی و مقاومت های برشی و خمشی نمونه های تیر در این مطالعه بررسی شده است و کاربرد آن در طراحی ها نیز در نظر گرفته شده است. نتایج نشان میدهد که ظرفیت انتقال بار بر روی این سطوح کاهش پیدا میکند که این موضوع به دلیل تکانه خمشی در قسمت دهانه ترک میباشد، اما هیچ تاثیری بر روی مقاومت برشی و خمشی در نمونه های تیر وجود ندارد. اما، انعطاف پذیری خمشی مورد دوم نسبتا به دلیل لغزش برشی کاهش یافته است که بعد از شکل گفتن لولا های پلاستیکی رخ میدهد و سقوط منطقه های فشرده شده ایجاد میشود. نمیتوان صحت عبارات طراحی را برای پیش بینی بیشترین مقاومت اصطکاک ارزیابی کرد. اما، کاربرد عمومی این عبارات در این شرایط هنوز باید بررسی شود، زیرا این عبارات نمیتوانند کاهش مقاومت که بعد از تورق لایه های تقویت طولی رخ میدهد را پیش بینی کنند.
6- جمع بندی |
| بخشی از مقاله انگلیسی |
|
Abstract The shear strength of concrete-to-concrete interfaces subjected to either shear or normal forces perpendicular to the interface, or to a combination of both, has been predicted using the “shear-friction theory” developed in the 60’s for connections for the precast construction. The “shear-friction theory” has been developed considering shear failure as pure slippage, and not in combination with a tension crack, and it has been adopted in most design codes worldwide. Although several improvements have been made to the original theory in the last 50 years, few have addressed the behaviour of interfaces subjected to a combination of shear and bending moment, where a shear slippage may occur along a tension crack and a compression zone. This is a relevant issue for the design of both cast-in-place and precast reinforced concrete structures. This paper, presents an experimental work addressed to the study of the behaviour of concrete-to-concrete interfaces subjected to a combination of shear and bending moment. The influence of the interface on the global behaviour and shear and bending strengths of a beam specimen are addressed, as well as the application of the design expressions. Results show that the load transfer capacity across the interface is reduced due to the bending moment crack opening, but it has no influence on the shear and the bending strengths of the beam specimen. However, the bending ductility of the latter is partially reduced due to a shear slippage occurred after the formation of a plastic hinge, and the collapse of the compression zone. It was not possible to evaluate the accuracy of the design expressions to predict the interface maximum friction strength. However, the general application of these expressions to this situation is doubtful, as they are incapable to predict the strength deterioration occurred after the yielding of the longitudinal reinforcement.
6- Conclusions An experimental work was carried out in order to study the behaviour of concrete-to-concrete interfaces subjected to combination of shear and bending moment and to analyse the application of the design expressions based on the ‘‘shear-friction theory”. The effect of the interface in the shear strength, bending strength and ductility of a beam specimen was also analysed. Results show that neither the shear strength nor the bending strength of the specimens got affected by the presence of a casting interface. However, the reduced tension strength between the two differently aged concretes, which could be below that of the weakest concrete, lead to a premature cracking along the interface, in the tension zone. This phenomenon was mainly observed in the hogging region where the tension crack occurred firstly along the interface rather than over the support. The variation of the typical cracking pattern on the web, from diagonal to vertical, pointed to a reduced capacity of the interface to transfer shear loads towards the support, in relation to the reference specimen. This phenomenon did not affect the shear resistance but it was a determining factor in the shear slippage occurred after the formation of a plastic hinge over the continuous support. The crack width increase at the interface led to a deterioration of the mechanisms responsible for the load transfer (aggregate interlock and dowel action), conducting to a shear slippage along the flange in tension and the web, and to the development of a tension crack in the compressed flange. The global bending behaviour of the specimen was similar to the reference model, however with reduced ductility.
|
|
تصویری از مقاله ترجمه و تایپ شده در نرم افزار ورد |
|
|
| دانلود رایگان مقاله انگلیسی + خرید ترجمه فارسی | |
| عنوان فارسی مقاله: |
تحقیقات تجربی در رابطه با رفتار سطوح مشترک بین بتن – بتن تحت ترکیبی از تکانه های برشی و خمشی |
| عنوان انگلیسی مقاله: |
Experimental research on the behaviour of concrete-to-concrete interfaces subjected to a combination of shear and bending moment |
|
|
|