این مقاله انگلیسی ISI در نشریه ساینس دایرکت (الزویر) در 6 صفحه در سال 2016 منتشر شده و ترجمه آن 18 صفحه میباشد. کیفیت ترجمه این مقاله ویژه – طلایی ⭐️⭐️⭐️ بوده و به صورت کامل ترجمه شده است.
| دانلود رایگان مقاله انگلیسی + خرید ترجمه فارسی | |
| عنوان فارسی مقاله: |
برآورد نرخ FAC و ارزیابی عمر سرویس تحت داده های کنترل عملیاتی |
| عنوان انگلیسی مقاله: |
Substantiation of FAC rate and service life estimation under operation control data |
|
|
|
| مشخصات مقاله انگلیسی (PDF) | |
| سال انتشار | 2016 |
| تعداد صفحات مقاله انگلیسی | 6 صفحه با فرمت pdf |
| رشته های مرتبط با این مقاله | مهندسی مواد |
| گرایش های مرتبط با این مقاله | خوردگی و پوشش و حفاظت سطح مهندسی، خوردگی و حفاظت از مواد |
| چاپ شده در مجله (ژورنال) | انرژی هسته ای و فناوری – Nuclear Energy and Technology |
| کلمات کلیدی | پوشش خوردگی جریان شتابدار، رسوب محصولات خوردگی، داده های اندازه گیری ضخامت، روش محاسبه نرخ FAC، عمر باقیمانده، کمترین ضخامت مجاز |
| ارائه شده از دانشگاه | انستیتو Obninsk انرژی هسته ای، دانشگاه ملی تحقیقات هسته ای MEPhI، روسیه |
| نویسندگان | V.I. Baranenko , O.M. Gulina, N.L. Salnikovb , O.E. Murzina |
| شناسه شاپا یا ISSN | ISSN 2452-3038 |
| شناسه دیجیتال – doi | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nucet.2016.07.005 |
| دارد ✓ | |
| کد محصول | 9471 |
| لینک مقاله در سایت مرجع | لینک این مقاله در نشریه Elsevier |
| نشریه الزویر |  |
| مشخصات و وضعیت ترجمه فارسی این مقاله (Word) | |
| وضعیت ترجمه | انجام شده و آماده دانلود |
| کیفیت ترجمه | ویژه – طلایی ⭐️⭐️⭐️ |
| تعداد صفحات ترجمه تایپ شده با فرمت ورد با قابلیت ویرایش | 18 صفحه با فونت 14 B Nazanin |
| ترجمه عناوین جداول | ترجمه شده است ✓ |
| ترجمه متون داخل جداول | ترجمه شده است ✓ |
| درج جداول در فایل ترجمه | درج شده است ✓ |
| درج فرمولها و محاسبات در فایل ترجمه | به صورت عکس درج شده است ✓ |
| منابع داخل متن | به صورت عدد درج شده است ✓ |
| فهرست مطالب |
|
چکیده مقدمه مروری بر رویکردهای مورد استفاده در NPP های روسی و خارجی برای ارزیابی نرخ FAC ضرایب تصحیح محاسبه عمر باقی مانده خط لوله ها روش پیشنهاد شده برای محاسبه نرخ FAC و عمر باقی مانده خطوط لوله مربوط به NPP های بومی تحلیل داده های کنترلی بر مبنای روش توسعه یافته نتیجه گیری |
| بخشی از ترجمه |
|
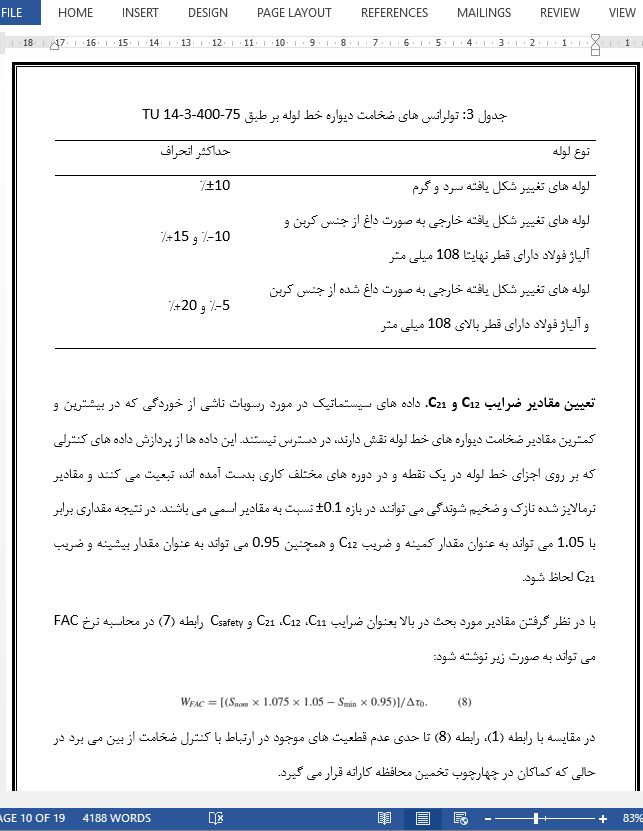
چکیده خوردگی پوشش ناشی از جریان شتابدار (FAC) مکانیزم پیچیده ای از خرابی المان های (عناصر) تجهیزات NNP و خطوط لوله است. نرخ FAC با فاکتورهایی نظیر خوردگی فلز، جریان هیدرودینامیک، هندسه عناصر تجهیزات و خطوط لوله، رژیم های شیمیایی آب اعمال شده (WCR)، طول مدت کارکرد، ترکیب شیمیایی فلز، ضخامت فیلم (غشای) رسوب کرده ناشی از خوردگی و عوامل دیگر مشخص می شود. رویکردهایی برای ارزیابی نرخ FAC بر طبق داده های کنترلی در این تحقیق درج شده اند. تحقیقات با هدف تعیین روشی برای محاسبه نرخ FAC صورت گرفته است. عدم وجود روشی برای محاسبه نرخ FAC، اجازه تایید برنامه های محاسباتی را نمیدهد که این موضوع منجر به استفاده از داده های اسناد قانونی بر حسب کمترین ضخامت مجاز [1] برای تعیین عمر باقیمانده می شود. پردازش داده های اندازی گیری شده امکان تعیین شاخص های اصلی فرایند FAC همانند مقادیر نازک و ضخیم شدن دیواره، نرخ نازک و ضخیم شدن دیواره، مدت زمان کارکد باقیمانده برای رسیدن به کمترین ضخامت مجاز را فراهم نمود. کاهش ضخامت بر اثر خوردگی فلز و افزایش آن بر اثر تشکیل فیلم رسوب که این رسوب خود محصول خوردگی می باشد، ایجاد می شود.
نتیجه گیری |
| بخشی از مقاله انگلیسی |
|
Abstract Flow-accelerated corrosion (FAC) wear is the complex mechanism of damage of elements of NPP equipment and pipelines. FAC rate is determined by such factors as corrosion of metal, flow hydrodynamics, geometry of equipment elements and pipelines, applied water chemistry regimes (WCR), duration of operation, chemical composition of the metal, thickness of deposited corrosion product film and others. Approaches to the assessment of FAC rate according to the control data are addressed in the present study. Implemented investigation was aimed at the substantiation of the methodology of calculation of FAC rate. Absence of the methodology for calculation of FAC rate does not allow verification of calculation programs, as well as the use of data of regulatory documents on the minimum permissible thicknesses [1] for evaluating the residual lifetime. Processing of measured data allowed determining the main indexes of FAC process such as the values of wall thinning and thickening, rates of wall thinning and thickening, residual operation time to the moment of reaching the minimum permissible thickness. Reduction of thickness is determined by corrosion of metal and its increase is determined by the formation of deposited film of corrosion products.
Conclusion 1. Trend of increasing minimum wall thicknesses obtained during sequential measurements and, correspondingly, increasing residual life time is revealed on the basis of analysis of repeated measurements performed on Unit 1 of NPP Dukovany in the Czech Republic. Increase of wall thickness as compared to the nominal one can reach as high as 30%. This fact must be taken into account in the development of methodology for calculation of FAC rates for metals. 2. Calculation dependence for determining the metal FAC rate incorporating the correction coefficients taking into account the effects of technological tolerances on the wall thickness due to pipeline manufacturing, as well as effects of corrosion products deposits on the values of initial and minimum wall thicknesses was suggested. 3. It is showing that using the suggested methodology for feed water pipelines elements with standard dimensions equal to 530×28 mm and to 426×24 mm for one of NPP unit with VVER reactor results in the increase of estimated residual life time by approximately 2.2 times for bends and by 3.14 times for straight parts. 4. Thus, conservative estimation of residual life time leaves sufficient time for implementation of repeated measurements on the problematic elements and for making decisions on the replacement of the elements.
|
|
تصویری از مقاله ترجمه و تایپ شده در نرم افزار ورد |
|
|
| دانلود رایگان مقاله انگلیسی + خرید ترجمه فارسی | |
| عنوان فارسی مقاله: |
برآورد نرخ FAC و ارزیابی عمر سرویس تحت داده های کنترل عملیاتی |
| عنوان انگلیسی مقاله: |
Substantiation of FAC rate and service life estimation under operation control data |
|
|
|